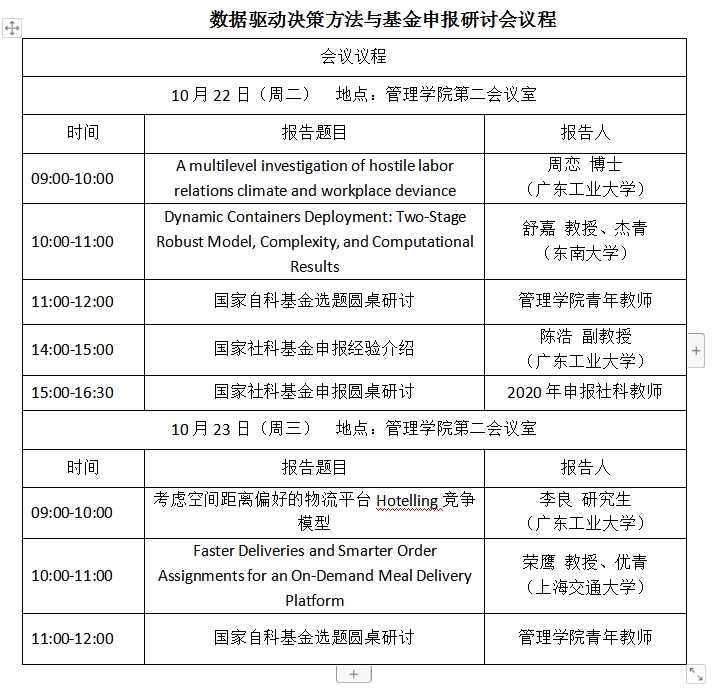
数据驱动的决策与运营优化是近年来重要的研究热点,管理学院特邀请校外专家做主题报告和学术指导。2019年10月22日-23日邀请东南大学经济管理学院舒嘉教授、上海交通大学安泰经济与管理学院荣鹰教授分别做主题报告和基金申报圆桌研讨。欢迎全体有兴趣的教师和研究生参加,特别欢迎学院2020年申报国家基金的教师参加会议研讨!
研讨会议程安排如下:
主题报告嘉宾
舒嘉博士,东南大学经济管理学院教授、博士生导师、副院长,2012年获国家优秀青年科学基金,2015年获国家杰出青年科学基金,2016年4月入选教育部青年人才。研究方向为:物流与供应链管理,交通管理,医疗管理。主持国家自然科学基金、教育部归国留学人员科研启动基金和教育部新世纪优秀人才支持计划等多项课题,学术成果发表在Operations Research, Transportation Science, Naval Research Logistics等国际权威期刊上。
报告内容简介(Abstract):Containers are widely used in the shipping industry mainly because of their capability to facilitate multimodal transportation. How to effectively reposition the nonrevenue empty containers is the key to reduce the cost and improve the service in the liner shipping industry. In this paper, we propose a two-stage robust optimization model that takes into account the laden containers routing as well as the empty container repositioning, and define the robustness for this model with uncertainties in the supply and demand of the empty containers. Based on this definition, we present the robust formulations for the uncertainty sets corresponding to theℓp-norm, wherep= 1, 2, and ∞, and analyze the computational complexities for all of these formulations. The only polynomial-time solvable case corresponds to theℓ1-norm, which we use to conduct the numerical study. We compare our approach with both the deterministic model and the stochastic model for the same problem in the rolling horizon simulation environment. The computational results establish the potential practical usefulness of the proposed approach.
荣鹰博士,现任上海交通大学安泰经济与管理学院教授、博士生导师,2015年度国家优秀青年科学基金资助。他于2010年8月回国执教于上海交通大学,此前在美国加州大学伯克利分校和里海大学从事科研工作,并在上海交通大学和美国里海大学分别获学士、硕士和博士学位。主要研究领域为服务运营优化、新兴商业模型的运作以及数据驱动的优化模型。研究成果发表在Management Science, Operations Research,Manufacturing & Service Operations Management, Production and Operations Management, Naval Research Logistics, IIE Transactions等国际学术刊物上。荣鹰教授多次获得过国际奖项,其中包括两度MSOM最佳论文奖和INFORMS Energy, Natural Resources & Environment Young Researcher Prize。
报告内容简介(Abstract):The focus of this talk is to identify the underlying factors and develop an order assignment policy that can help an on-demand meal delivery service platform to grow. By analyzing transactional data obtained from an online meal delivery platform in Hangzhou (China) over a two-month period in 2015, we find empirical evidence that an ``early delivery'' is positively correlated with customer retention: a 10-minute earlier delivery is associated with an increase of one order per month from each customer. However, we find that the negative effect on future orders associated with ``late deliveries'' is much stronger than the positive effect associated with early deliveries. Moreover, we show empirically that a driver's individual local area knowledge and prior delivery experience can reduce late deliveries significantly. Finally, through a simulation study, we illustrate how one can incorporate our empirical results in the development of an order assignment policy that can help a platform to grow its business through customer retention. Our empirical results and our simulation study suggest that to increase future customer orders, an on-demand service platform should address the issues arising from both the supply side (i.e., driver's local area knowledge and delivery experience) and the demand side (i.e., asymmetric impacts of early and late deliveries on customer future orders) into their operations.